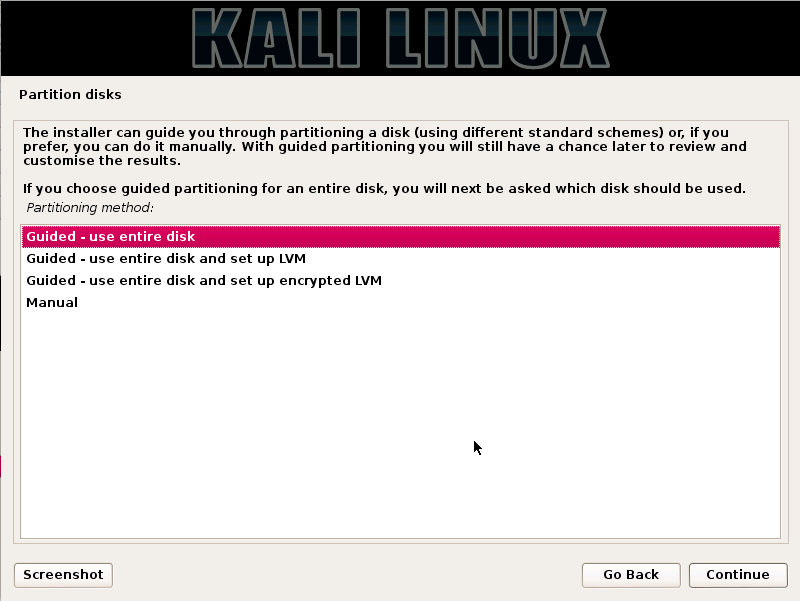
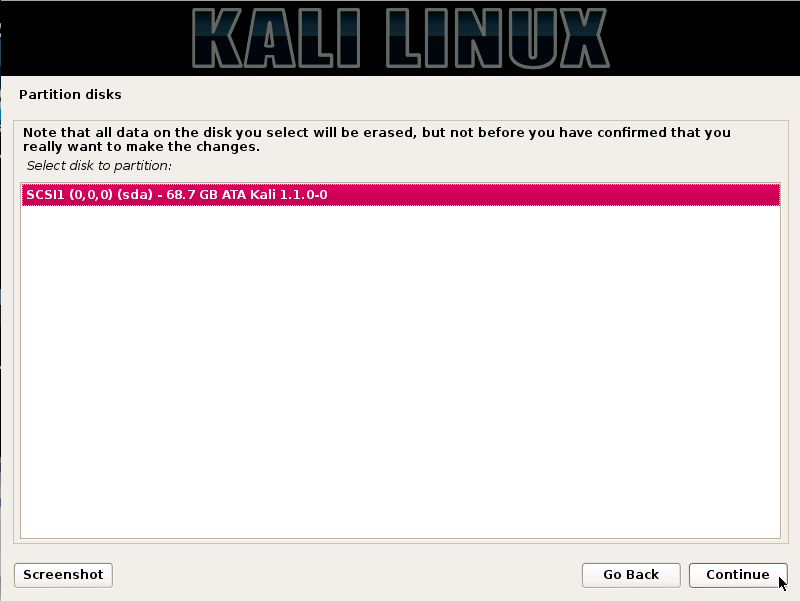
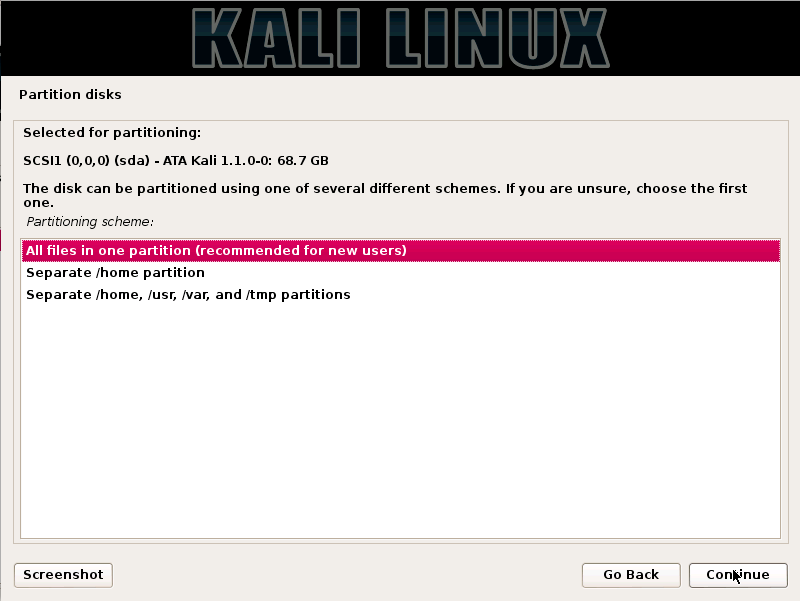
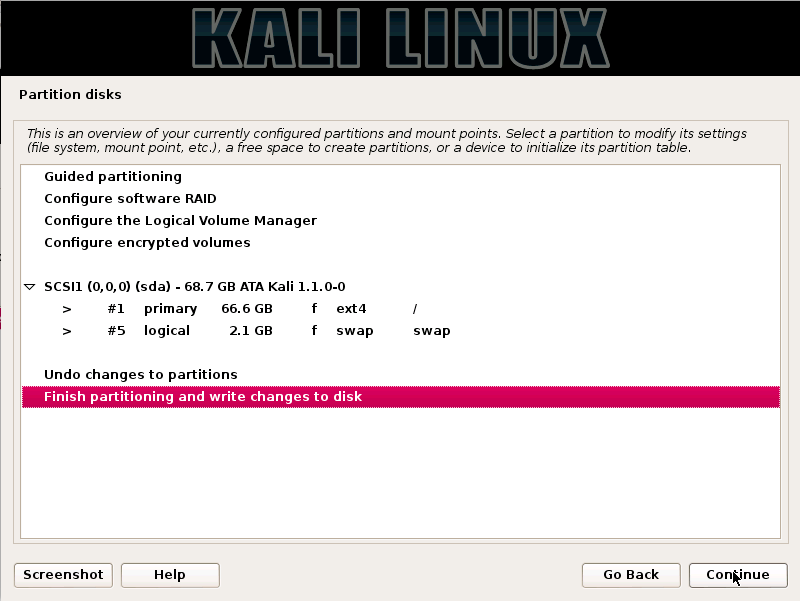
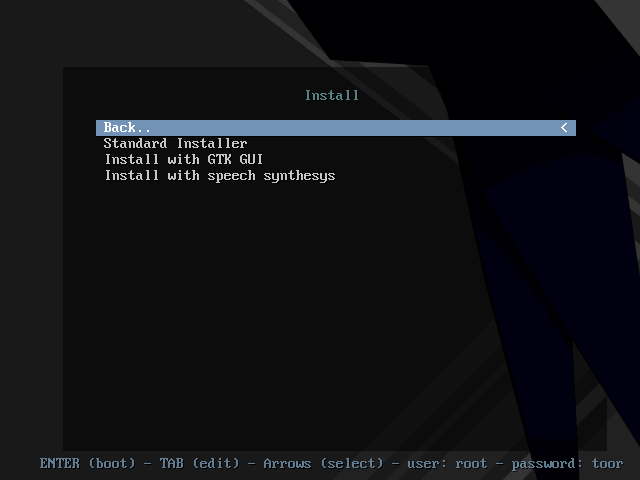
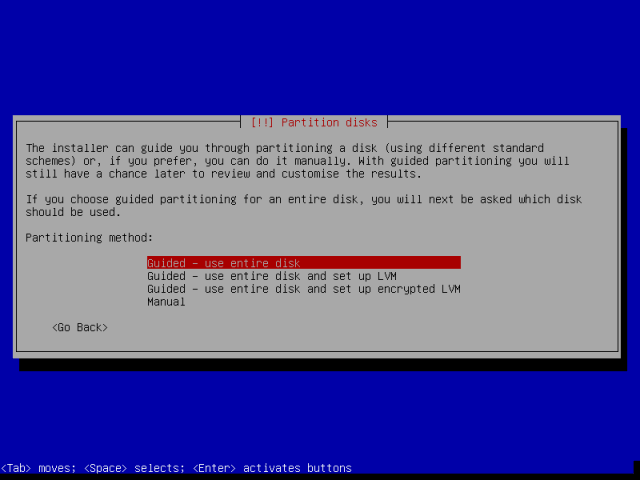
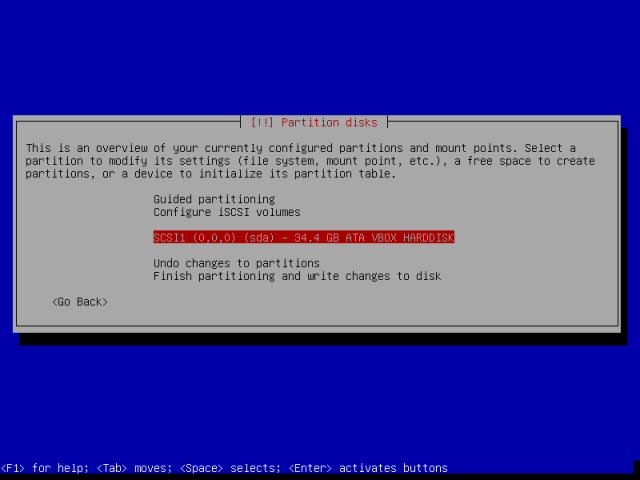
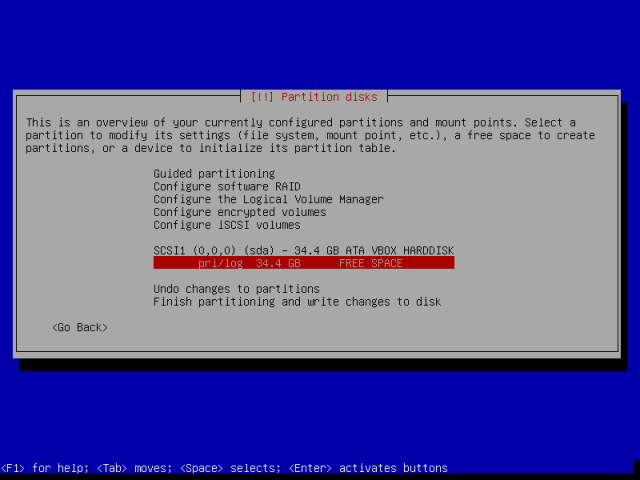
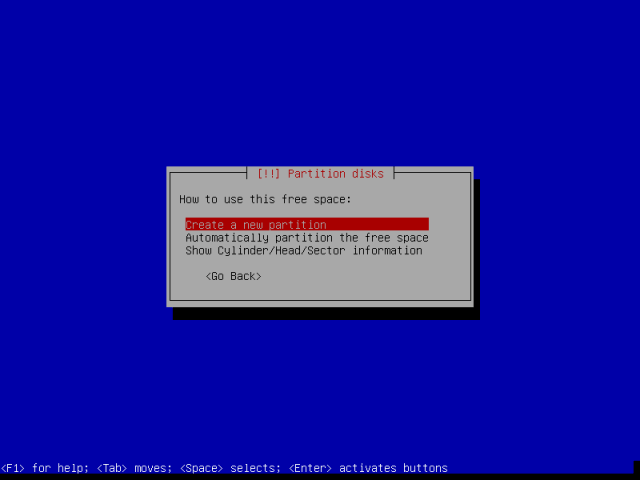
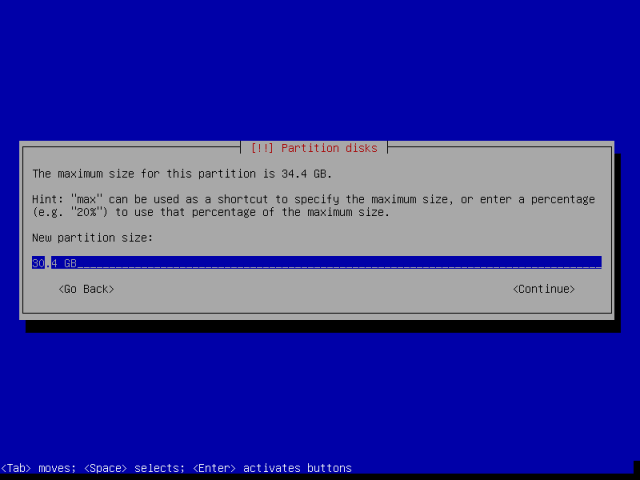
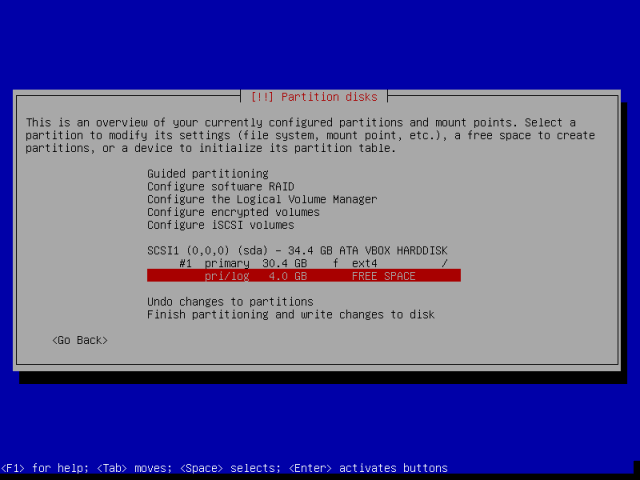
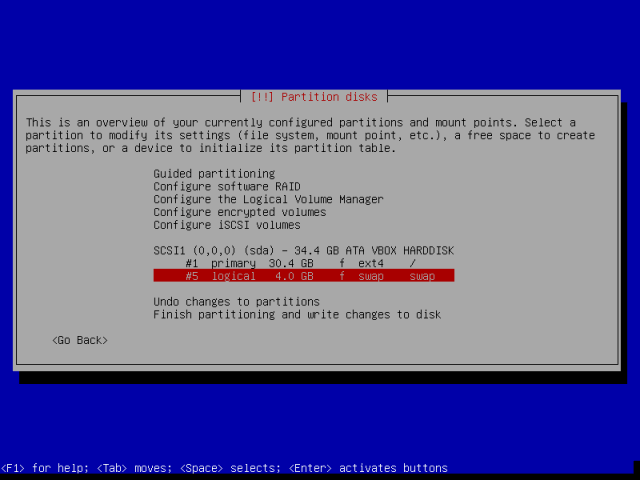
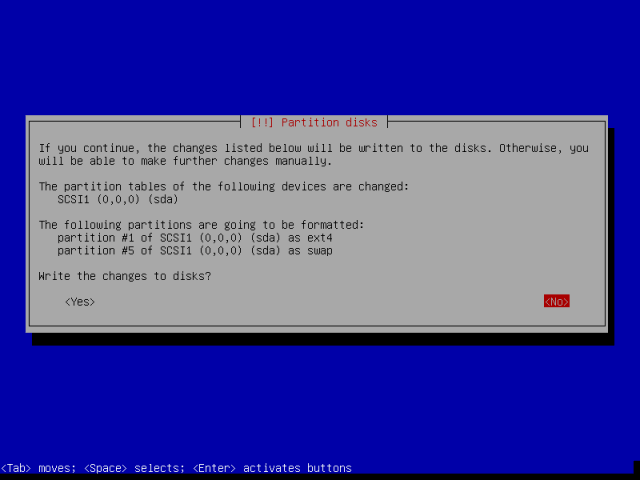
A hacker is a highly skilled computer operator who uses bugs and exploits to break into computer systems and networks. An ethical hacker, on the other hand, identifies vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks, and plugs these holes. Here’s a round-up of the ten best operating systems for ethical hackers and penetration testers.
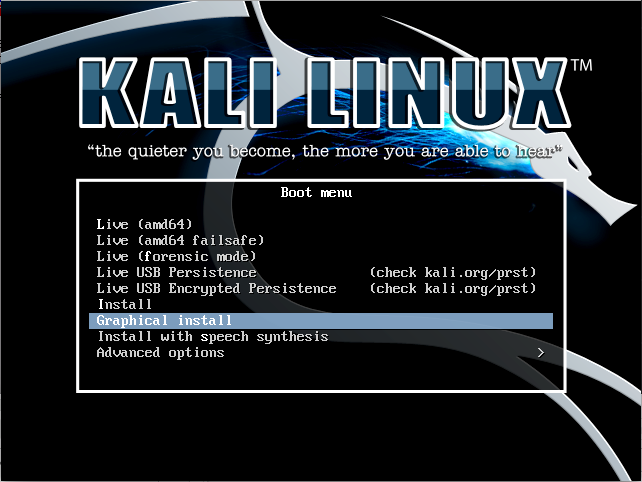
1.KALI LINUX

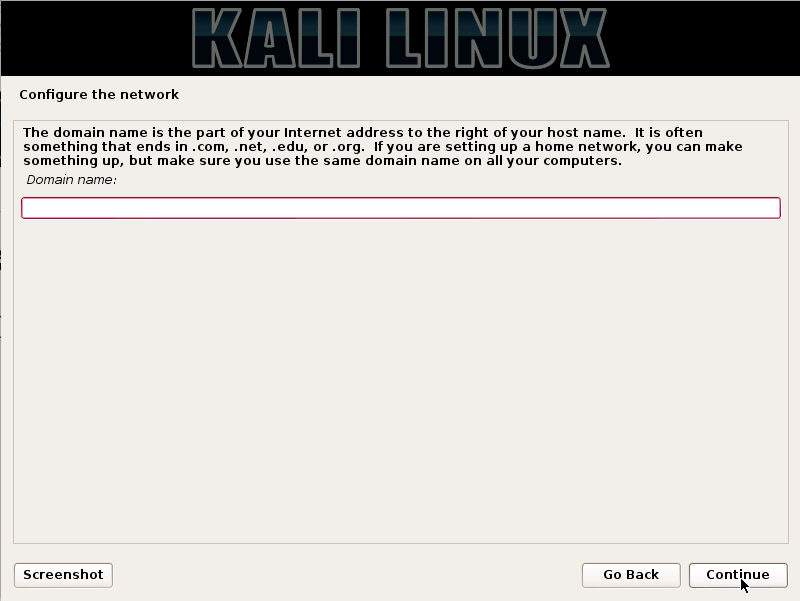
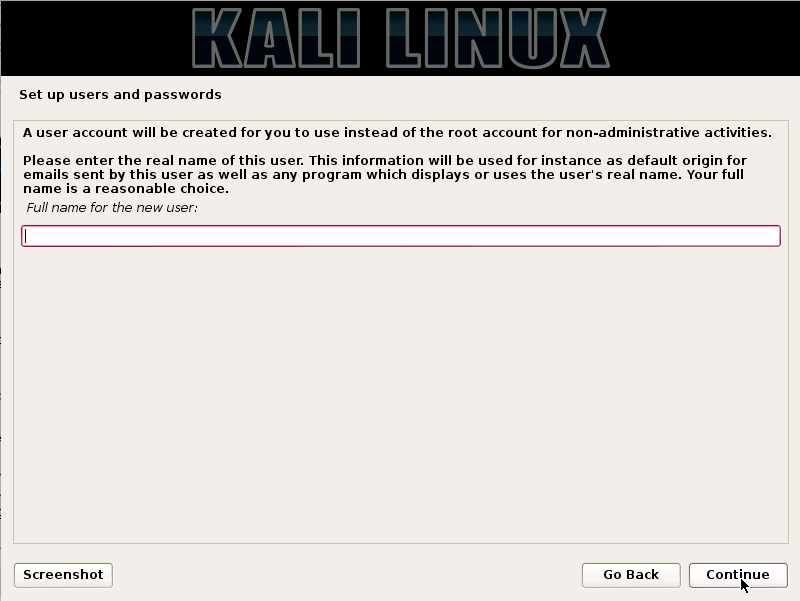
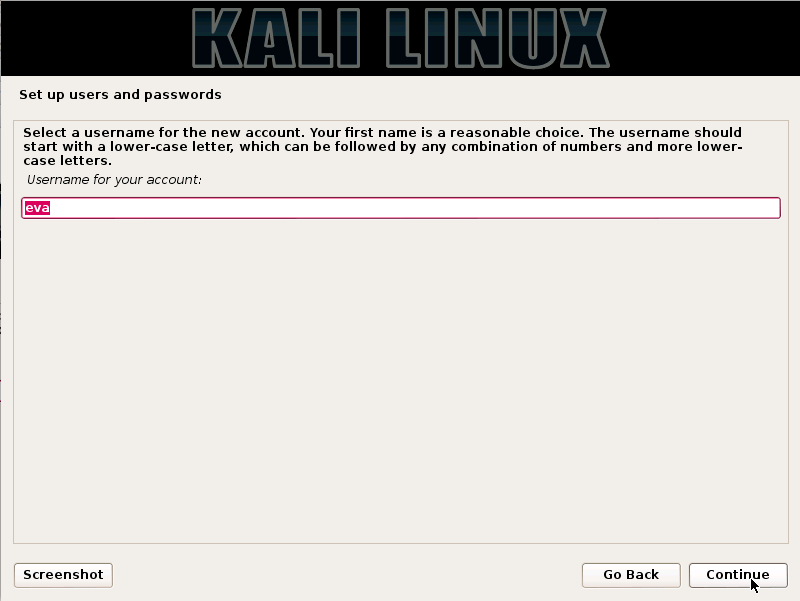
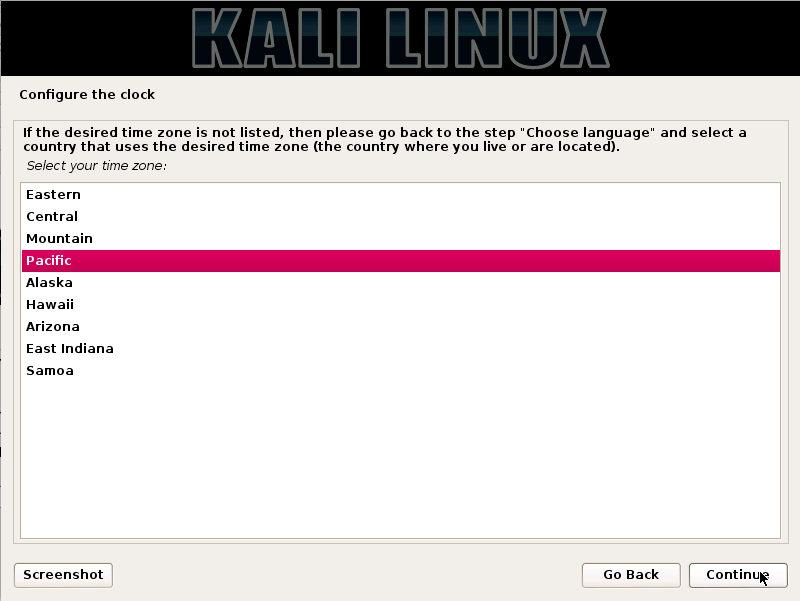
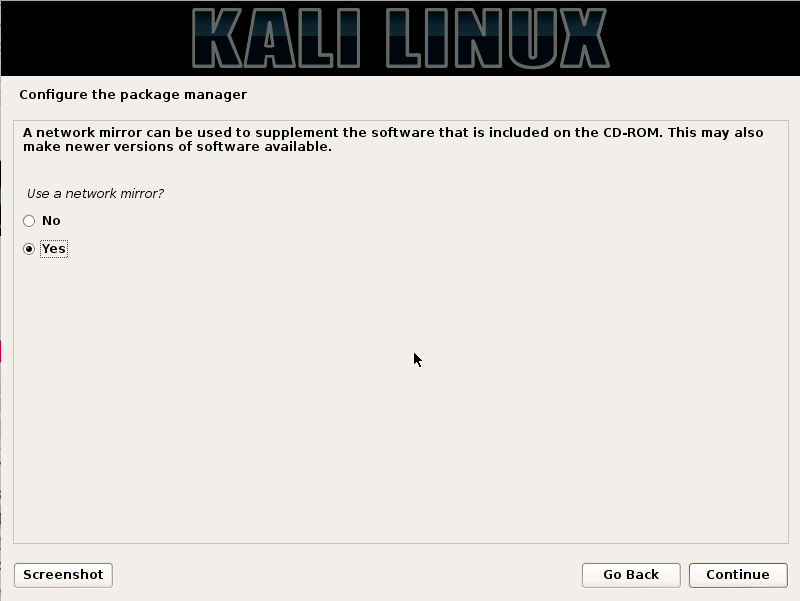
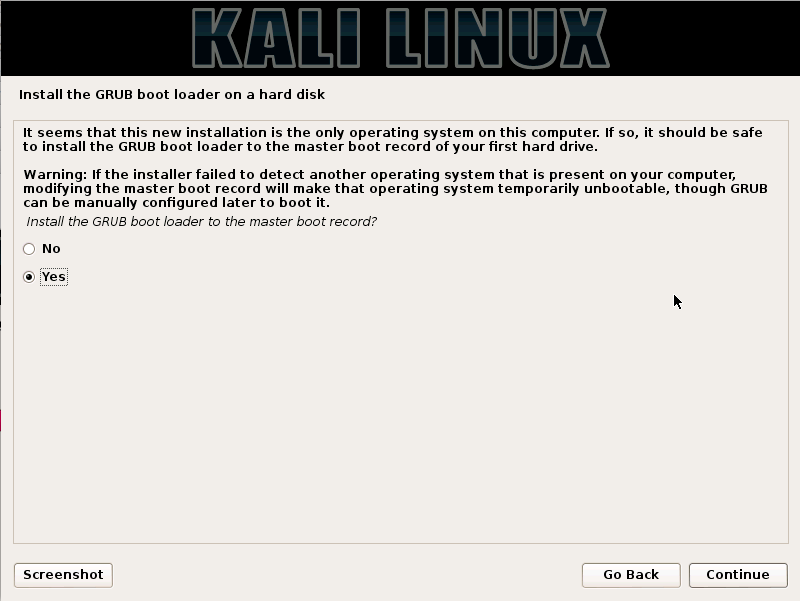
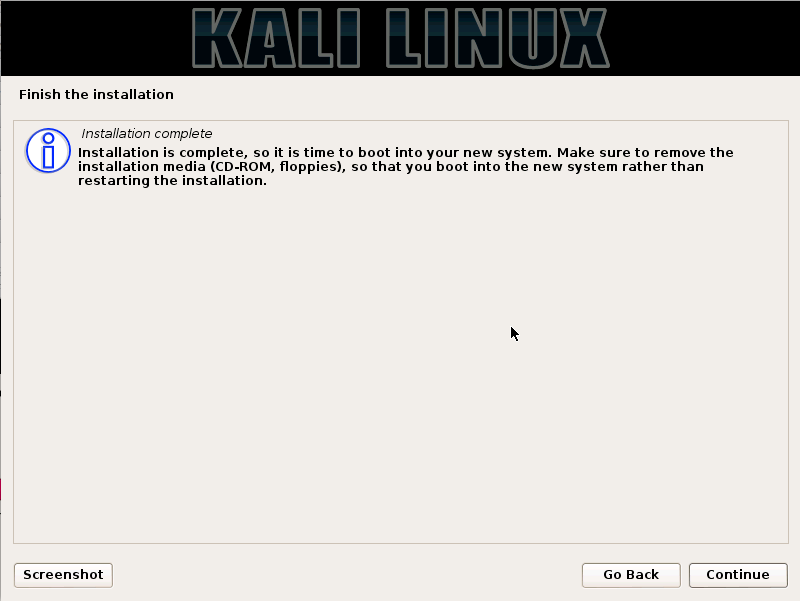
Kali Linux is based on the Debian-Linux distribution, and is especially designed for digital forensics and penetration testing.
It is maintained and updated on a regular basis by Offensive Security Ltd, under the leadership of Mati Aharoni, Devon Kearns and Raphael Hertzog who are core developers. https://www.kali.org/downloads/
Kali comes pre-installed with more than 300 penetration testing programs and can be installed as a primary operating system on the hard disk, live CD/USB and can even run as a virtual machine using some virtualisation software.
2.BackBox
BackBox is an Ubuntu-based Linux distribution aimed at assisting ethical hackers and penetration testers in security assessments. BackBox OS is designed with the objective of being faster, easily operable and having a minimal desktop environment. The key advantage of BackBox is that its own software repositories are updated at regular intervals to keep the distribution stable and popular for real-world operations. https://www.backbox.org/download/
The BackBox distribution consists of more than 70 tools for tasks ranging from Web analysis and network analysis to stress testing, sniffing, vulnerability assessment, forensics and exploitation.

3. PARROT SECURITY OPERATING SYSTEM
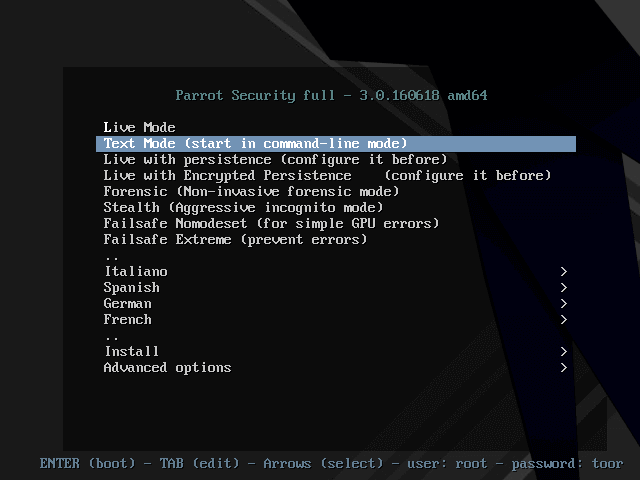
Parrot Security OS is based on Debian GNU/Linux combined with the Frozenbox OS and Kali Linux to provide ethical hackers the best-in-class experience of penetration and security testing in real-world environments. It is also designed to provide vulnerability assessment and mitigation, computer forensics and anonymous Web browsing, by the Frozenbox team.
Parrot Security OS makes use of Kali repositories for all sorts of package updates and to integrate new tools. It makes use of the MATE desktop environment using the LightDM display manager to provide an easy-to-use GUI and lightweight environment for computer system analysts to perform all sorts of forensics, vulnerability assessment and cryptography. This OS is known for being highly customisable and for its strong community support.

for download .. https://parrotsec.org/download/
Equipped with the highly customisable kernel version 4.5, it is currently under rolling release upgrade line and based on Debian 9.Has custom anti-forensic tools, interfaces for GPG, Cryptsetup, and support for LUKS, Truecrypt and VeraCrypt.
It supports FALCON 1.0 programming language, multiple compilers, debuggers and the Qt5 and .NET/mono frameworks.Supports Anonsurf including anonymisation of the entire OS, TOR, I2P anonymous networks and beyond.
A special edition of Parrot Cloud, designed for servers, comprises lightweight Parrot OS distributions without graphics, wireless and forensics tools, and acts as a VPS or dedicated server with only useful security tools.
4. DEFT LINUX
DEFT (Digital Evidence and Forensics Toolkit) is based on GNU Linux and DART (Digital Advanced Response Toolkit), a forensics system comprising some of the best tools for forensics and incident response. DEFT Linux is especially designed for carrying out forensics tasks and runs live on systems without tampering with the hard disk or any other storage media. http://www.deftlinux.net/
It consists of more than 100 highly-rated forensics and hacking tools.It is currently developed and maintained by Stefano Fratepietro along with other developers, and is available free of charge. It is used actively by ethical hackers, pen testers, government officers, IT auditors and even the military for carrying out various forensics based systems analysis.
It is based on the Lubuntu distribution comprising open source digital forensics and penetration testing tools http://iso.linuxquestions.org/deft-linux/
Full support for Bitlocker encrypted disks, Android and iOS 7.1 logical acquisitions.Consists of Digital Forensics Framework 1.3.
5. SAMURAI WEB TESTING FRAMEWORK
Samurai Web Testing Framework primarily focuses on testing the security of Web applications and comprises lots of Web assessment and exploitation tools. The credit for developing the Samurai Web Testing Framework goes to Kevin Johnson, Justin Searle and Frank DiMaggio. The Samurai Framework provides ethical hackers and pen testers with a live Linux environment that is preconfigured to run as a virtual machine to perform Web penetration testing. http://www.samurai-wtf.org/
The Samurai Web Testing Framework includes popular testing tools like Fierce Domain Scanner and Maltego for Reconnaissance, WebScarab and Ratproxy for mapping, w3af and Burp for discovery, and BeEF and AJAXShell for exploitation.

The framework is based on Ubuntu 9.04, is fully open source and receives regular updates with regard to products.Contains many tools for reconnaissance, mapping, discovery and exploitation, especially focusing on Web penetration testing.Equipped with SVN to provide updated security tools, and syncs with active development tools.