PHP Tutorial
- PHP Tutorial
- Install PHP
- PHP Code
- PHP Echo and print
- PHP Variable
- PHP Variable Scope
- PHP $ and $$
- PHP Constants
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Operators
- PHP Comments
Control Statement
- PHP If else
- PHP Switch
- PHP For Loop
- PHP foreach loop
- PHP While Loop
- PHP Do While Loop
- PHP Break
- PHP Continue
PHP Functions
- PHP Functions
- Parameterized Function
- PHP Call By Value and reference
- PHP Default Arguments
- PHP Variable Arguments
- PHP Recursive Function
PHP Arrays
PHP Strings
PHP Math
PHP Form
PHP Include
State Management
PHP File
Upload Download
PHP OOPs Concepts
- OOPs Concepts
- OOPs Abstract Class
- OOPs Abstraction
- OOPs Access Specifiers
- OOPs Const Keyword
- OOPs Constructor and destructor
- Encapsulation
- Final Keyword
- OOPs Functions
- OOPs Inheritance
- OOPs Interface
- OOPs Overloading
- OOPs Type Hinting
PHP MySQLi
- MySQLi CONNECT
- MySQLi CREATE DB
- MySQLi CREATE Table
- MySQLi INSERT
- MySQLi UPDATE
- MySQLi DELETE
- MySQLi SELECT
- MySQLi Order by
PHP Topics
- Compound Types
- is_null() Function
- Special Types
- Inheritance Task
- Special Types
- MVC Architecture
- PHP vs. JavaScript
- PHP vs. HTML
- PHP vs. Node.js
- PHP vs Python
- PHP PDO
- Top 10 PHP frameworks
- phpMyAdmin
- Count All Array Elements
- Create Newline
- Get Current Page URL
PHP Mail
- Encapsulation is a concept where we encapsulate all the data and member functions together to form an object.
- Wrapping up data member and method together into a single unit is called Encapsulation.
- Encapsulation also allows a class to change its internal implementation without hurting the overall functioning of the system.
- Binding the data with the code that manipulates it.
- It keeps the data and the code safe from external interference.
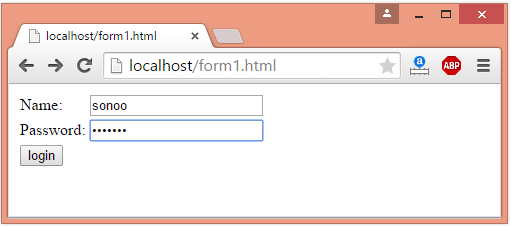
Example 1
<?php
class person
{
public $name;
public $age;
function __construct($n, $a)
{
$this->name=$n;
$this->age=$a;
}
public function setAge($ag)
{
$this->ag=$ag;
}
public function display()
{
echo "welcome ".$this->name."<br/>";
return $this->age-$this->ag;
}
}
$person=new person("sonoo",28);
$person->setAge(1);
echo "You are ".$person->display()." years old";
?>
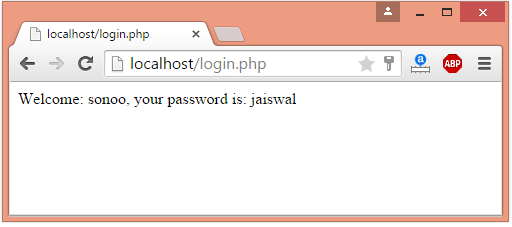
Output:
Welcome sonoo
You are 27 years old