PHP Tutorial
- PHP Tutorial
- Install PHP
- PHP Code
- PHP Echo and print
- PHP Variable
- PHP Variable Scope
- PHP $ and $$
- PHP Constants
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Operators
- PHP Comments
Control Statement
- PHP If else
- PHP Switch
- PHP For Loop
- PHP foreach loop
- PHP While Loop
- PHP Do While Loop
- PHP Break
- PHP Continue
PHP Functions
- PHP Functions
- Parameterized Function
- PHP Call By Value and reference
- PHP Default Arguments
- PHP Variable Arguments
- PHP Recursive Function
PHP Arrays
PHP Strings
PHP Math
PHP Form
PHP Include
State Management
PHP File
Upload Download
PHP OOPs Concepts
- OOPs Concepts
- OOPs Abstract Class
- OOPs Abstraction
- OOPs Access Specifiers
- OOPs Const Keyword
- OOPs Constructor and destructor
- Encapsulation
- Final Keyword
- OOPs Functions
- OOPs Inheritance
- OOPs Interface
- OOPs Overloading
- OOPs Type Hinting
PHP MySQLi
- MySQLi CONNECT
- MySQLi CREATE DB
- MySQLi CREATE Table
- MySQLi INSERT
- MySQLi UPDATE
- MySQLi DELETE
- MySQLi SELECT
- MySQLi Order by
PHP Topics
- Compound Types
- is_null() Function
- Special Types
- Inheritance Task
- Special Types
- MVC Architecture
- PHP vs. JavaScript
- PHP vs. HTML
- PHP vs. Node.js
- PHP vs Python
- PHP PDO
- Top 10 PHP frameworks
- phpMyAdmin
- Count All Array Elements
- Create Newline
- Get Current Page URL
PHP Mail
To create a newline, PHP provides nl2br() function. It is an in-built function of PHP, which is used to insert the HTML line breaks before all newlines in the string. Although, we can also use PHP newline character \n or \r\n inside the source code to create the newline, but these line breaks will not be visible on the browser. So, the nl2br() is useful here.
The nl2br() function contains these newline characters \n or \r\n which combinely create the newline. Apart from nl2br() function, a html break line tag </br> is used to break the string. The </br> tag should be enclosed in double quotes, e.g., “</br>”.
For Example
To create the newline in PHP, let’s see the number of examples.
Example 1
Let’s take an of example to create the newline with the help of nl2br() function.
- <?php
- echo nl2br(“New line will start from here\n in this string\r\n on the browser window”);
- ?>
Output
In this example, we can see that the nl2br() function has contained “\n” and “\r\n” characters in the string for newline. We can see the result of the following program in the below output.
New line will start from here in this string on the browser window
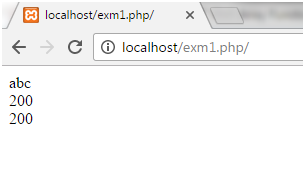
Example 2
<?php
echo "One line after\n another line";
echo " One line after\r\n another line";
?>
Output
In the above example, we can see that after “\n” or “\r\n” character, string did not start from the new line. “\n” and “\r\n” alone are not enough for creating a newline in the string, as the whole string is displayed in a single line.
One line after another line One line after another line
Note: The character “/n” is used in Linux to write a newline whereas in windows “\r\n” is used. For the safe side use the “\r\n” character for creating newline instead.
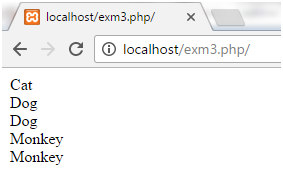
Example 3
<?php
echo "One line after\n another line";
echo "</br>";
echo "One line after\r\n another line";
?>
Output
Here, we break the lines using html break line tag “</br>“.
One line after another line One line after another line