PHP Tutorial
- PHP Tutorial
- Install PHP
- PHP Code
- PHP Echo and print
- PHP Variable
- PHP Variable Scope
- PHP $ and $$
- PHP Constants
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Operators
- PHP Comments
Control Statement
- PHP If else
- PHP Switch
- PHP For Loop
- PHP foreach loop
- PHP While Loop
- PHP Do While Loop
- PHP Break
- PHP Continue
PHP Functions
- PHP Functions
- Parameterized Function
- PHP Call By Value and reference
- PHP Default Arguments
- PHP Variable Arguments
- PHP Recursive Function
PHP Arrays
PHP Strings
PHP Math
PHP Form
PHP Include
State Management
PHP File
Upload Download
PHP OOPs Concepts
- OOPs Concepts
- OOPs Abstract Class
- OOPs Abstraction
- OOPs Access Specifiers
- OOPs Const Keyword
- OOPs Constructor and destructor
- Encapsulation
- Final Keyword
- OOPs Functions
- OOPs Inheritance
- OOPs Interface
- OOPs Overloading
- OOPs Type Hinting
PHP MySQLi
- MySQLi CONNECT
- MySQLi CREATE DB
- MySQLi CREATE Table
- MySQLi INSERT
- MySQLi UPDATE
- MySQLi DELETE
- MySQLi SELECT
- MySQLi Order by
PHP Topics
- Compound Types
- is_null() Function
- Special Types
- Inheritance Task
- Special Types
- MVC Architecture
- PHP vs. JavaScript
- PHP vs. HTML
- PHP vs. Node.js
- PHP vs Python
- PHP PDO
- Top 10 PHP frameworks
- phpMyAdmin
- Count All Array Elements
- Create Newline
- Get Current Page URL
PHP Mail
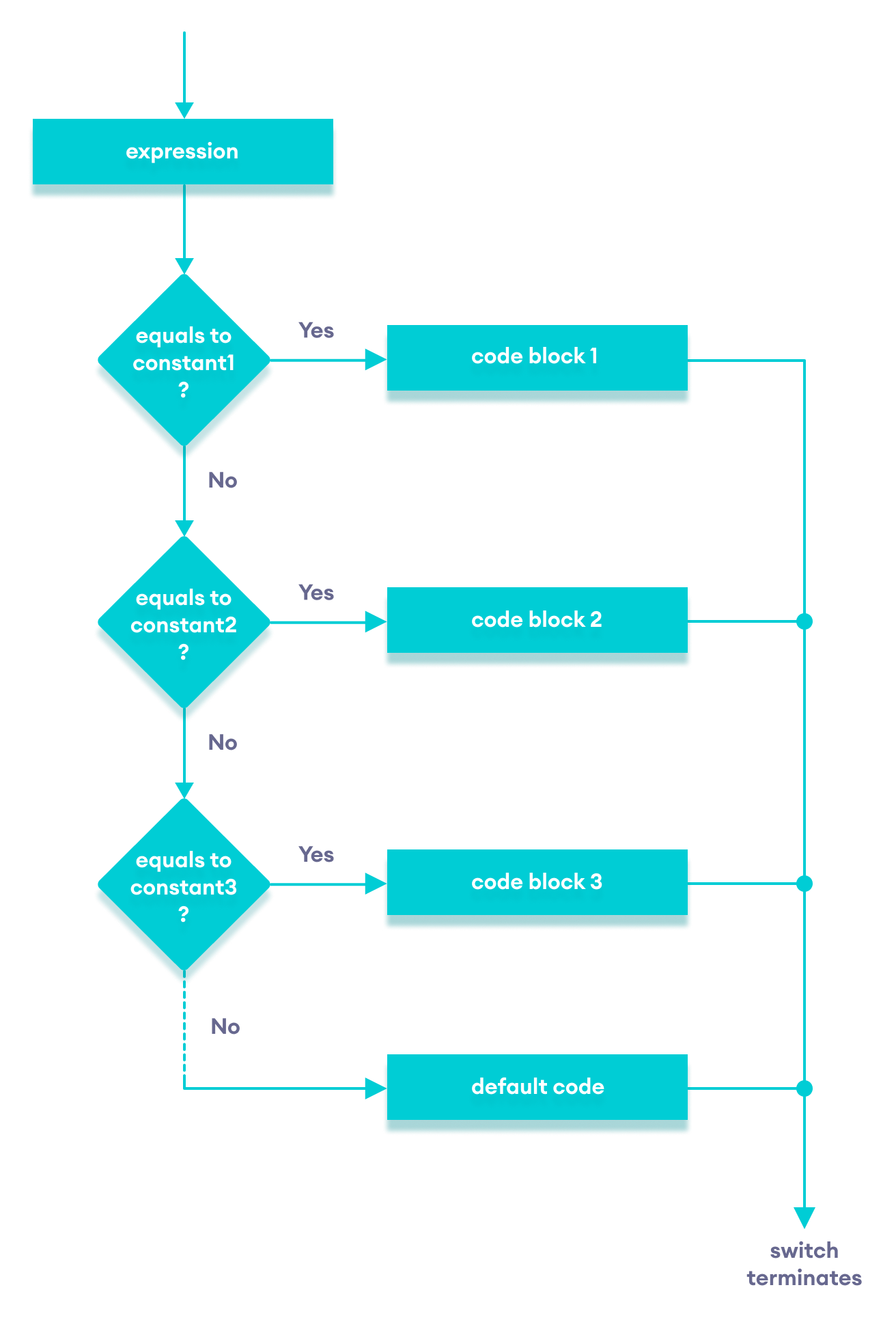
PHP switch statement is used to execute one statement from multiple conditions. It works like PHP if-else-if statement.
Syntax
switch(expression){
case value1:
//code to be executed
break;
case value2:
//code to be executed
break;
......
default:
code to be executed if all cases are not matched;
}
Important points to be noticed about switch case:
- The default is an optional statement. Even it is not important, that default must always be the last statement.
- There can be only one default in a switch statement. More than one default may lead to a Fatal error.
- Each case can have a break statement, which is used to terminate the sequence of statement.
- The break statement is optional to use in switch. If break is not used, all the statements will execute after finding matched case value.
- PHP allows you to use number, character, string, as well as functions in switch expression.
- Nesting of switch statements is allowed, but it makes the program more complex and less readable.
- You can use semicolon (;) instead of colon (:). It will not generate any error.
PHP Switch Example
<?php
$num=20;
switch($num){
case 10:
echo("number is equals to 10");
break;
case 20:
echo("number is equal to 20");
break;
case 30:
echo("number is equal to 30");
break;
default:
echo("number is not equal to 10, 20 or 30");
}
?>
Output:
number is equal to 20
PHP switch statement with character
Program to check Vowel and consonant
We will pass a character in switch expression to check whether it is vowel or constant. If the passed character is A, E, I, O, or U, it will be vowel otherwise consonant.
<?php
$ch = 'U';
switch ($ch)
{
case 'a':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'e':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'i':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'o':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'u':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'A':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'E':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'I':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'O':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
case 'U':
echo "Given character is vowel";
break;
default:
echo "Given character is consonant";
break;
}
?>
Output:
Given character is vowel
PHP switch statement with String
PHP allows to pass string in switch expression. Let’s see the below example of course duration by passing string in switch case statement.
<?php
$ch = "B.Tech";
switch ($ch)
{
case "BCA":
echo "BCA is 3 years course";
break;
case "Bsc":
echo "Bsc is 3 years course";
break;
case "B.Tech":
echo "B.Tech is 4 years course";
break;
case "B.Arch":
echo "B.Arch is 5 years course";
break;
default:
echo "Wrong Choice";
break;
}
?>
Output:
B.Tech is 4 years course
PHP switch statement is fall-through
PHP switch statement is fall-through. It means it will execute all statements after getting the first match, if break statement is not found.
<?php
$ch = 'c';
switch ($ch)
{
case 'a':
echo "Choice a";
break;
case 'b':
echo "Choice b";
break;
case 'c':
echo "Choice c";
echo "</br>";
case 'd':
echo "Choice d";
echo "</br>";
default:
echo "case a, b, c, and d is not found";
}
?>
Output:
Choice c Choice d case a, b, c, and d is not found
PHP nested switch statement
Nested switch statement means switch statement inside another switch statement. Sometimes it leads to confusion.
<?php
$car = "Hyundai";
$model = "Tucson";
switch( $car )
{
case "Honda":
switch( $model )
{
case "Amaze":
echo "Honda Amaze price is 5.93 - 9.79 Lakh.";
break;
case "City":
echo "Honda City price is 9.91 - 14.31 Lakh.";
break;
}
break;
case "Renault":
switch( $model )
{
case "Duster":
echo "Renault Duster price is 9.15 - 14.83 L.";
break;
case "Kwid":
echo "Renault Kwid price is 3.15 - 5.44 L.";
break;
}
break;
case "Hyundai":
switch( $model )
{
case "Creta":
echo "Hyundai Creta price is 11.42 - 18.73 L.";
break;
case "Tucson":
echo "Hyundai Tucson price is 22.39 - 32.07 L.";
break;
case "Xcent":
echo "Hyundai Xcent price is 6.5 - 10.05 L.";
break;
}
break;
}
?>
Output:
Hyundai Tucson price is 22.39 - 32.07 L.